Selenium is one of the oldest browser automation tools, and it’s still widely used. If you already have Selenium in your stack, you can take screenshots without adding another dependency. Let me quickly show you how.
If you don’t want to read and just save time,I created a dedicated repository with tested and working examples of how to take screenshots with Selenium in Python.
However, if you don’t use Selenium and building from scratch, I recommend using Playwright instead, it is a modern and actively developed library for browser automation. Especially if that’s the only functionality you need. Or check out our guide to how to take website screenshots Python.
Quick Start
Install Selenium and webdriver-manager:
pip install selenium webdriver-managerUsing webdriver-manager eliminates the need to manually download ChromeDriver:
from selenium import webdriverfrom selenium.webdriver.chrome.service import Service as ChromeServicefrom webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager
# automatically download and use the correct ChromeDriverdriver = webdriver.Chrome(service=ChromeService(ChromeDriverManager().install()))
driver.get('https://example.com')driver.save_screenshot('screenshot.png')driver.quit()If you are familiar with example.com, you should not be surprised by the result:
Screenshot Methods
Selenium provides three ways to capture screenshots:
1. Save to File
driver.save_screenshot('screenshot.png')2. Get as Bytes (PNG)
png_bytes = driver.get_screenshot_as_png()
# Save manuallywith open('screenshot.png', 'wb') as f: f.write(png_bytes)3. Get as Base64 String
base64_string = driver.get_screenshot_as_base64()
# Useful for embedding in HTML or sending via APIimport base64png_bytes = base64.b64decode(base64_string)Waiting for Page Load
Taking a screenshot too early means incomplete content:
Explicit Wait for Elements
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWaitfrom selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as ECfrom selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
driver.get('https://example.com')
# Wait for specific element to be visiblewait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10)wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '.main-content')))
driver.save_screenshot('screenshot.png')Fixed Timeout
import time
driver.get('https://example.com')time.sleep(3) # Wait 3 secondsdriver.save_screenshot('screenshot.png')Combine Both
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWaitfrom selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as ECfrom selenium.webdriver.common.by import Byimport time
driver.get('https://example.com')
# Wait for main contenttry: wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.TAG_NAME, 'body')))except: pass
# Extra buffer for JavaScripttime.sleep(1)
driver.save_screenshot('screenshot.png')Element Screenshots
Capture a specific element instead of the full viewport:
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
driver.get('https://example.com')
# Find element and screenshot itelement = driver.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR, '.hero-section')element.screenshot('hero.png')Viewport Settings
Control the browser window size:
# Set window size before navigatingdriver.set_window_size(1920, 1080)driver.get('https://example.com')driver.save_screenshot('screenshot.png')Or maximize:
driver.maximize_window()Full Page Screenshots
This is where Selenium falls short. Unlike Playwright, Selenium doesn’t have native full-page support. Here’s the workaround:
from selenium import webdriverfrom selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Optionsfrom PIL import Imageimport ioimport time
def full_page_screenshot(driver, output_path, scroll_wait): metrics = driver.execute_script( """ const body = document.body; const html = document.documentElement; const totalHeight = Math.max( body.scrollHeight, body.offsetHeight, body.clientHeight, html.scrollHeight, html.offsetHeight, html.clientHeight ); const viewportHeight = window.innerHeight; return { totalHeight, viewportHeight }; """ ) total_height = int(metrics["totalHeight"]) viewport_height = int(metrics["viewportHeight"]) if viewport_height <= 0: raise RuntimeError("Viewport height is zero") last_scroll = max(total_height - viewport_height, 0) positions = list(range(0, total_height, viewport_height)) if not positions or positions[-1] != last_scroll: positions.append(last_scroll) screenshots = [] for offset in positions: driver.execute_script( "document.documentElement.scrollTo(0, arguments[0]);" "document.body.scrollTo(0, arguments[0]);", offset, ) time.sleep(scroll_wait) png = driver.get_screenshot_as_png() screenshots.append(Image.open(io.BytesIO(png))) if not screenshots: raise RuntimeError("No screenshots captured") scale = screenshots[0].height / viewport_height total_height_px = int(total_height * scale) total_width_px = screenshots[0].width stitched = Image.new("RGB", (total_width_px, total_height_px)) y = 0 for img in screenshots: remaining = total_height_px - y if remaining <= 0: break if img.height > remaining: img = img.crop((0, 0, img.width, remaining)) stitched.paste(img, (0, y)) y += img.height stitched.save(output_path)
options = Options()options.add_argument('--headless')driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)driver.set_window_size(1920, 1080)driver.get('https://screenshotone.com')full_page_screenshot(driver, 'fullpage.png', 0.2)driver.quit()It did screenshot the full page, but it had some issue. E.g. it screenshots scrollbar, you can try to fix that by executing the following JavaScript code:
document.body.style.overflow = "hidden";Another issue was that the top navigation bar appeared in the screenshot a few times:
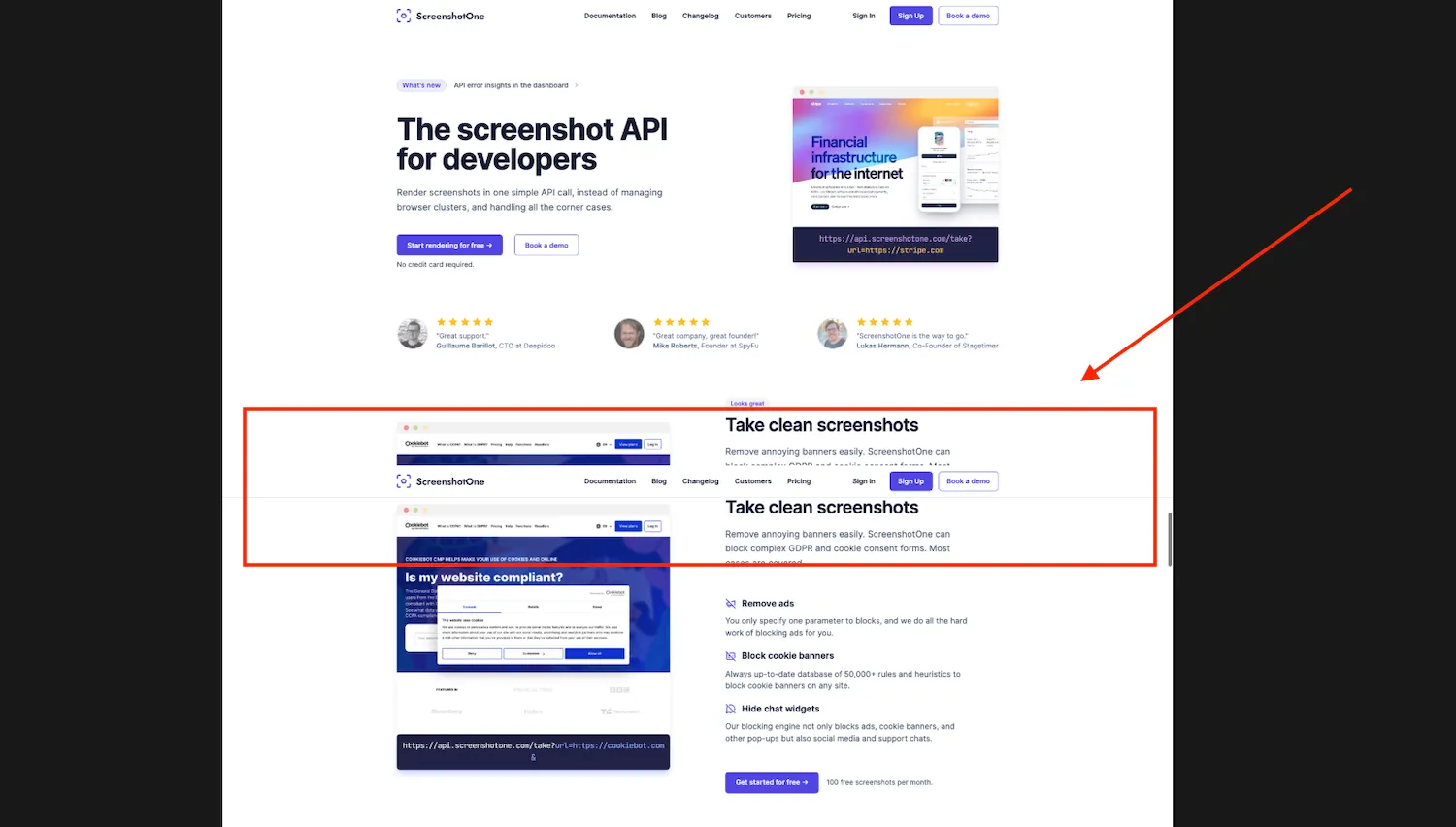
There are many ways to fix that:
- Try to fixate all the elements.
- Do not stitch pages together, but take a screenshot of the whole page by applying different techniques. However that will also have its own issues.
But unfortunately, it is out of the scope of this guide. Check out our Playwright (Python) guide to how to take full page screenshots for some examples on that can be solved.
If full-page screenshots is a critical part of your workflow, consider using our API instead.
Headless Mode
For server environments:
from selenium import webdriverfrom selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
options = Options()options.add_argument('--headless')options.add_argument('--no-sandbox')options.add_argument('--disable-dev-shm-usage')options.add_argument('--disable-gpu')options.add_argument('--window-size=1920,1080')
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)driver.get('https://example.com')driver.save_screenshot('screenshot.png')driver.quit()Chrome Options for Screenshots
Useful options for screenshot automation:
options = Options()options.add_argument('--headless')options.add_argument('--window-size=1920,1080')options.add_argument('--hide-scrollbars')options.add_argument('--force-device-scale-factor=2') # Retinaoptions.add_argument('--lang=en-US')options.add_argument('--disable-extensions')Error Handling
from selenium import webdriverfrom selenium.common.exceptions import TimeoutException, WebDriverExceptionfrom selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWaitfrom selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as ECfrom selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
def safe_screenshot(url, output_path): driver = None try: driver = webdriver.Chrome() driver.set_window_size(1920, 1080)
driver.get(url)
# Wait for page wait = WebDriverWait(driver, 10) wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.TAG_NAME, 'body')))
driver.save_screenshot(output_path) return True
except TimeoutException: print(f"Timeout loading {url}") return False except WebDriverException as e: print(f"WebDriver error: {e}") return False finally: if driver: driver.quit()Multiple Screenshots
Process multiple URLs:
from selenium import webdriverfrom selenium.webdriver.chrome.options import Options
urls = [ 'https://example.com', 'https://github.com',]
options = Options()options.add_argument('--headless')
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=options)driver.set_window_size(1920, 1080)
for i, url in enumerate(urls): try: driver.get(url) driver.implicitly_wait(5) driver.save_screenshot(f'screenshot_{i}.png') print(f'Success: {url}') except Exception as e: print(f'Failed: {url} - {e}')
driver.quit()Check our guide how to take bulk screenshots with Selenium in Python for more details.
Playwright vs Selenium for Screenshots
| Feature | Selenium | Playwright |
|---|---|---|
| Native full page | No | Yes |
| Async support | No | Yes |
| Element screenshots | Yes | Yes |
| Wait mechanisms | Explicit only | Multiple options |
| Setup complexity | Higher | Lower |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
My recommendation: If you’re starting fresh, use Playwright. If you already have Selenium in your project, it works fine for basic screenshots.
When to Use a Screenshot API
Selenium is fine for small volumes, but at scale:
- Browser process management becomes complex.
- Memory leaks are common.
- No native full-page support.
The best use case for that is when you perform testing of your websites: your run and screenshot pages and then close the browser and forget about resources. In that case, resource management is less of an issue.
For production workloads, consider a screenshot API like ScreenshotOne. See the main Python screenshot guide for all options.
Summary
Selenium screenshot basics:
- Use
save_screenshot()for simple saves - Use
webdriver-managerto avoid driver management. - Always wait for content before capturing.
- Full page requires workarounds (body element or scroll+stitch).
- Use headless mode for servers.
Frequently Asked Questions
If you read the article, but still have questions. Please, check the most frequently asked. And if you still have questions, feel free reach out at support@screenshotone.com.
How to take screenshot in Selenium Python?
Use driver.save_screenshot('screenshot.png') to save directly to file, or driver.get_screenshot_as_png() to get the screenshot as bytes for further processing.
How to take full page screenshot in Selenium Python?
Selenium doesn't have native full page support. You need to scroll through the page, capture sections, and stitch them together. Or use the body element screenshot method in headless mode.
What is the difference between save_screenshot and get_screenshot_as_png?
save_screenshot() saves directly to a file, while get_screenshot_as_png() returns the image as bytes. Use get_screenshot_as_png() when you need to process the image in memory.


