To add custom scripts to any page use Puppeteer’s page method page.addScriptTag(options).
You can inject:
- script by providing URL;
- script from the machine where the Puppeteer instance is running;
- raw script.
We are going to add a custom script to an example site:

We will change it with document.querySelector('h1').innerHTML = "Hello, world!";:
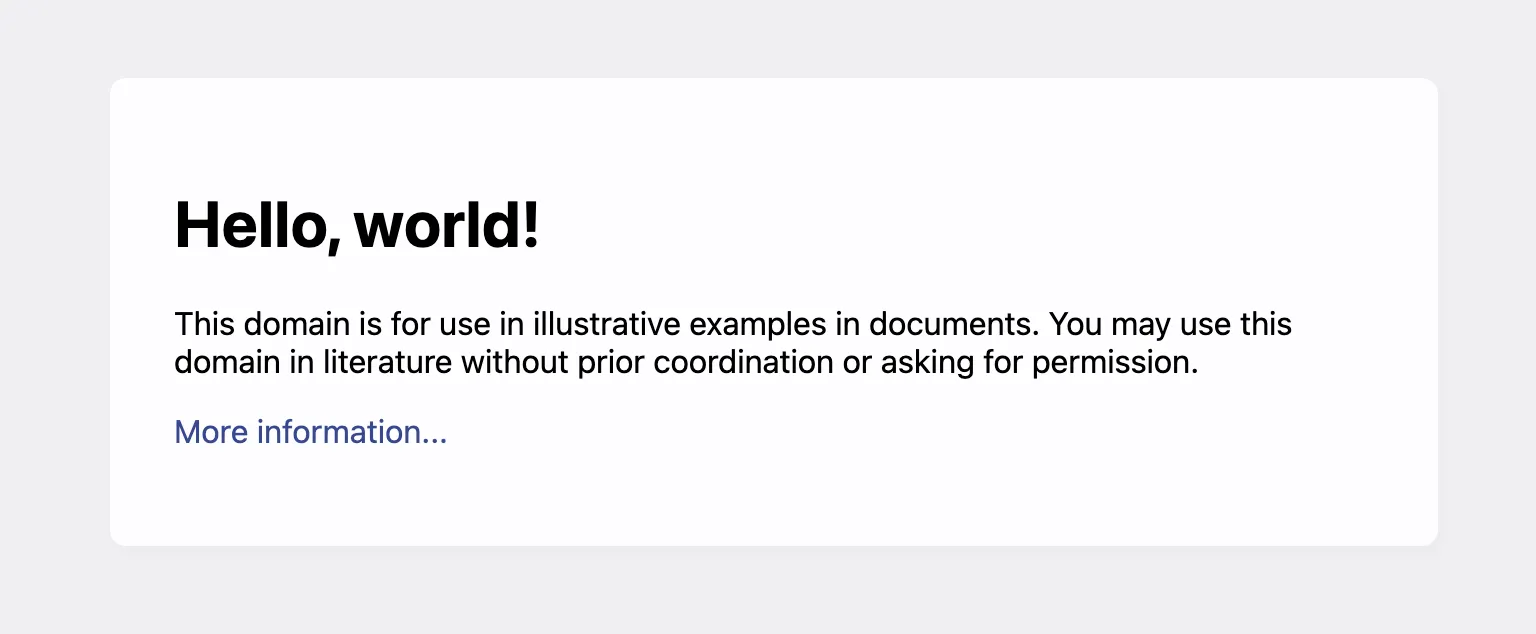
Let’s go!
Adding custom script by URL
To add custom script in Puppeteer by URL, use page.addScriptTag({url: 'https://example.com/custom.js'}):
As an example:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
(async () => { const browser = await puppeteer.launch({}); try { const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://example.com/');
await page.addScriptTag({ url: 'https://example.com/custom.js' });
await page.screenshot({ path: 'example.com.png' }); } catch (e) { console.log(e) } finally { await browser.close(); }})();```No need to worry and wait until the script file is included, because the promise for page.addScriptTag will resolve only when the added tag when the script’s onload event is fired.
Adding custom script by path
You also can add a custom stylesheet by specifying the path, use
page.addScriptTag({path: 'custom.js'}). If the path is relative, it is relative to the working directory.
As an example, I created custom.js:
h1 { color: red;}And then:
const puppeteer = require("puppeteer");
(async () => { const browser = await puppeteer.launch({}); try { const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto("https://example.com/");
await page.addScriptTag({ path: "custom.js" });
await page.screenshot({ path: "example.com.png" }); } catch (e) { console.log(e); } finally { await browser.close(); }})();Adding raw script content
In our screenshot API, you can easily add custom scripts by specifying the scripts parameter.
And the simplest way to add CSS custom style is just add raw CSS content by using page.addStyleTag({content: '<selector> { <property>: <value>; }'}):
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
(async () => { const browser = await puppeteer.launch({}); try { const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://example.com/');
await page.addScriptTag({ content: 'document.querySelector('h1').innerHTML = "Hello, world!"'});
await page.screenshot({ path: 'example.com.png' }); } catch (e) { console.log(e) } finally { await browser.close(); }})();I hope I helped you today to solve your problem and have a nice day 👋
You also might find helpful:


